Getting started cgroups for kubernetes resource requests and limits
Overview
There are many excellent articles or videos describing what is Kubernetes CPU resources requests and limits and how they are implemented. Watch followings to understand how the CPU resource requests and limits of a container on the Pod spec works on a Linux host with cgroup.
- Kaslin and Kohei’s video in CNCF in 2021
- Shon’s articles
{% comment %} https://blog.kintone.io/entry/2022/03/08/170206 https://medium.com/omio-engineering/cpu-limits-and-aggressive-throttling-in-kubernetes-c5b20bd8a718 https://engineering.squarespace.com/blog/2017/understanding-linux-container-scheduling {% endcomment %}
In short about CPU resources,
- K8s CPU resources are for CPU time, and not CPU cores.
- At a moment, a k8s pod might use all of CPU cores, beyond one set by CPU requests.
- If CPU limit is set
- Even if there is idle CPUs, they are not used if CPU usages hit the CPU limits
- k8s CPU resources are mapped on cgroups
- requests:
cpu.shares - limits:
cpu.cfs_quota_uswithcpu.cfs_period_us
- requests:
In this article, I’m going to check these cgroups configurations
Cgroups v1
Cgroups is to allow processes to have CPUs, memories, and network bandwidth.
Commands to work around Cgroups
- Check if my kernel supports it by confirming
/proc/cgroups. It’s supported if CPU or others are enabled there. - Install required tools by
sudo apt install cgroup-tools. - Create a cgroup by
sudo cgcreate -g cpu,memory:/my_cgroup- We can confirm the cgroup under
/sys/fs/cgroup/{cpu,memory}/my_cgroup
- We can confirm the cgroup under
- We can set some resource parameters there
sudo cgset -r cpu.cfs_quota_us=50000 my_cgroupto limit the CPU usages> cat /sys/fs/cgroup/cpu/my_group/cpu.cfs_quota_us 50000sudo cgset -r memory.limit_in_bytes=1G my_cgroupto limit the memory usages> cat /sys/fs/cgroup/memory/my_group/memory.limit_in_bytes 1073741824
- Add processes to the cgroup by adding some IDs on the file under the cgroup directory
- tasks: PIDs
- cgroup.procs: TGIDs (Thread Group IDs)
- Monitor usages
- CPU:
/sys/fs/cgroup/memory/my_group/cpu.stat. It’s described in the page, for example- nr_periods: number of period intervals
- nr_throttled: number of times tasks in a cgroup have been throttled
- throttled_time: the total time duration
- Memory:
/sys/fs/cgroup/memory/my_cgroup/memory.usage_in_bytes
- CPU:
- Delete the cgroup by
sudo cgdelete -g cpu,memory:/my_cgroup
Testings
There are good articles to test these configurations, including
I referred the above articles to test something further.
Load test CPUs
At first, prepare 2 cgroups, fast and slow.
Install stress beforehand.
- Create 2 cgroups
sudo cgcreate -g cpu:/fastsudo cgcreate -g cpu:/slow
- Set cpu.shares to assign 3:1 ratios between fast and slow
sudo cgset -r cpu.shares=750 fastsudo cgset -r cpu.shares=250 slow
Then load test CPUs on each cgroups for how it works.
Run a stress command with cgexec on the slow cgroup by next command. Note that 12 is the number of CPU cores on my machine.
> sudo cgexec -g cpu:slow stress --cpu 12 stress info: [1065] dispatching hogs: 12 cpu 0 io, 0 vm, 0 hddSee CPU usages by
htop. It’s confirmed that 12 CPUs are used for 100%.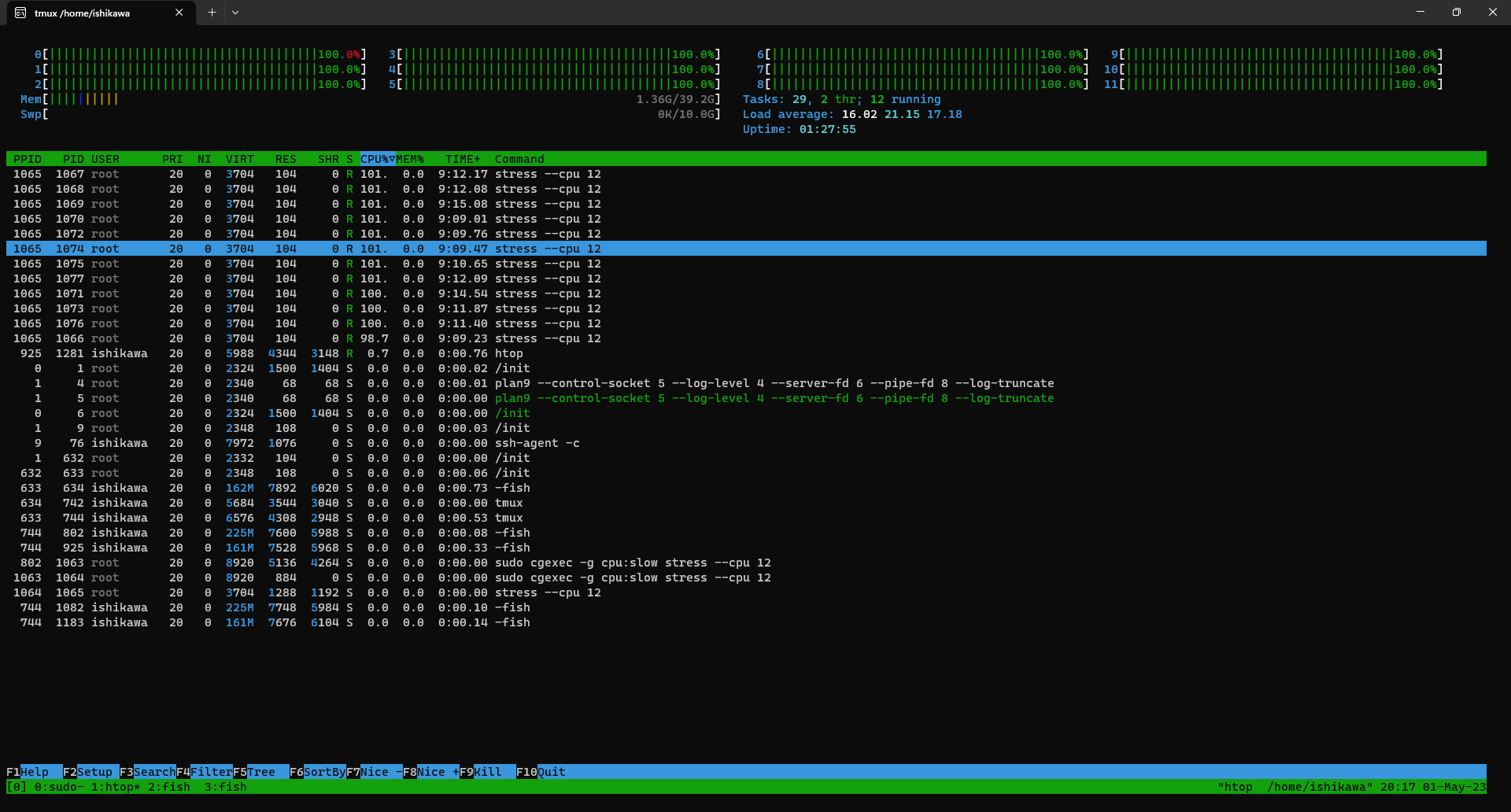
Run a stress on the fast cgroup by
> sudo cgexec -g cpu:fast stress --cpu 12 stress: info: [1305] dispatching hogs: 12 cpu, 0 io, 0 vm, 0 hddSee CPU usages by
htop. The PID output bystresscan be seen on the column PPID on htop to recognize which one is for fast cgroup and which one is for slow cgroup. And also, the fast cgroup uses about 75% (9 CPUs) while the slow cgroup uses 25% (3 CPUs), which is similar to the configuration ofcpu.sharesratios.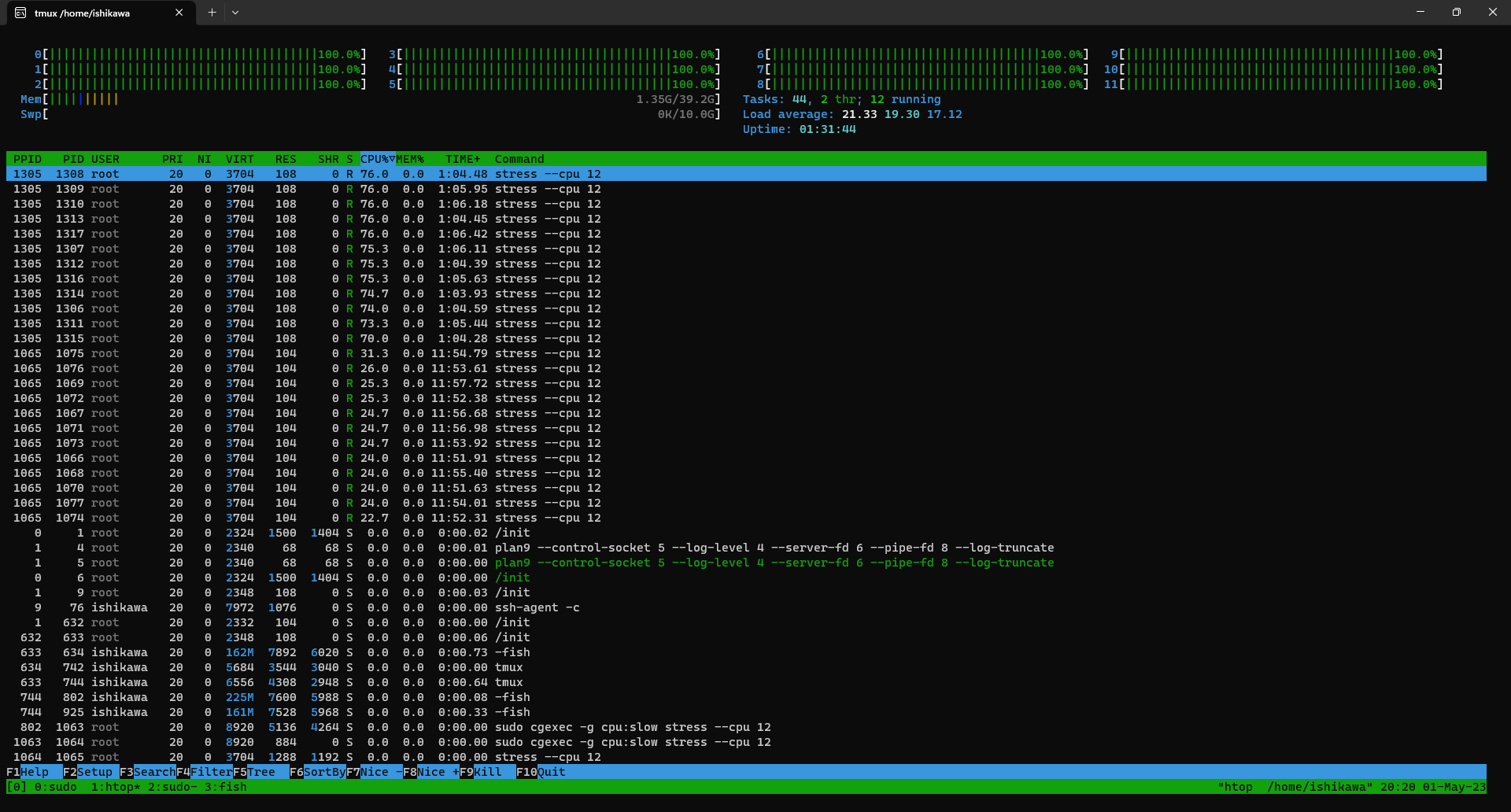
Confirm
cpu.cfs_quota_usandcpu.cfs_period_uson the fast cgroup.> sudo cgget -r cpu.cfs_quota_us fast fast: cpu.cfs_quota_us: -1 > sudo cgget -r cpu.cfs_period_us fast fast: cpu.cfs_period_us: 100000Set
cpu.cfs_quota_us to 400000to the fast cgroup so 4 CPUs are used per a second.> sudo cgset -r cpu.cfs_quota_us=400000 fast >See htop. CPU usages on the stress against the fast cgroup which PID=1305, was reduced and those for the slow cgroup was increased.
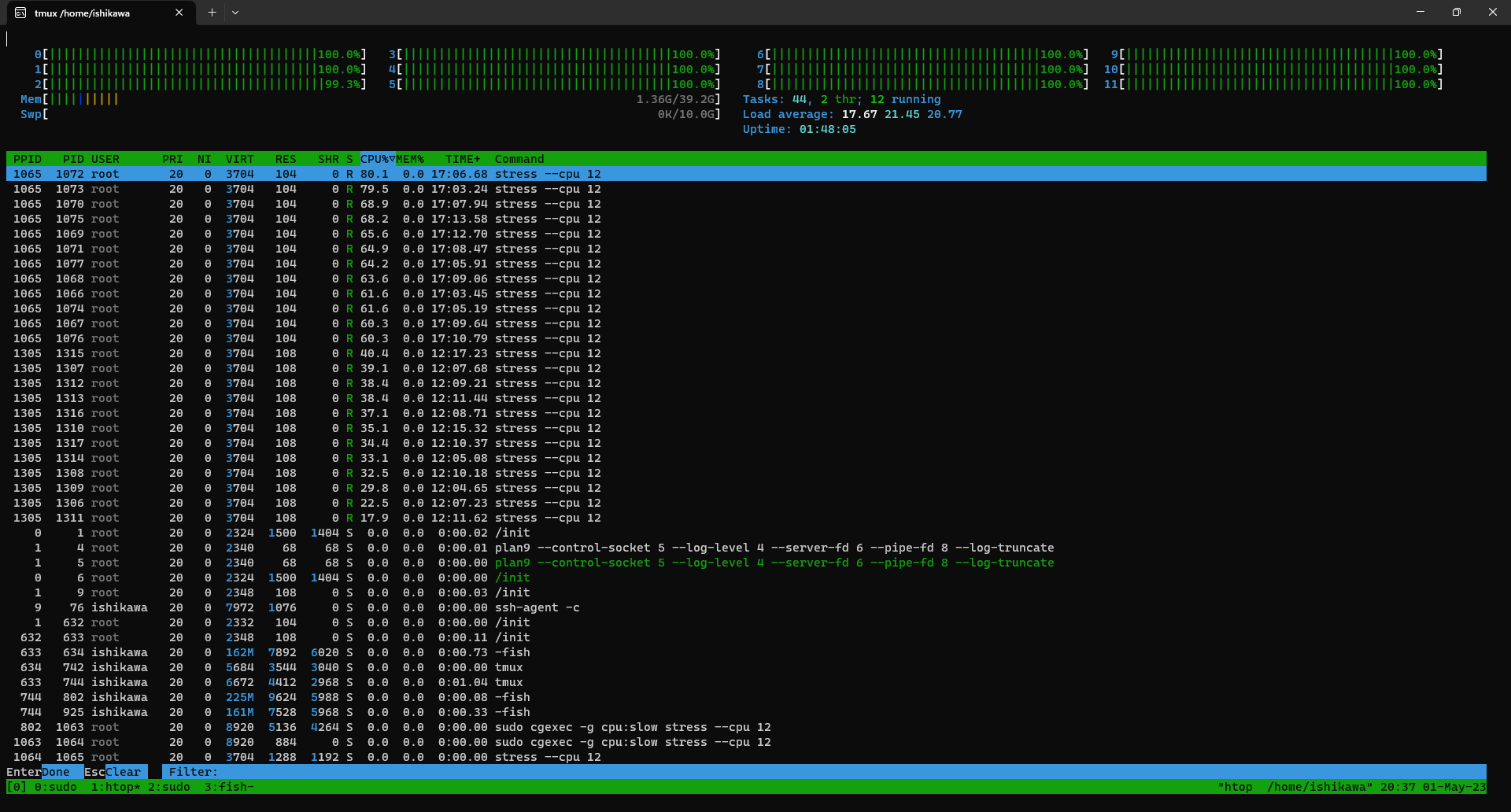
Stop the stress against the slow cgroup, which is without cpu.cfs_quota_us.
See htop. CPU usages on the stress against the fast cgroup cannot use 100% CPU usages. There are 12 CPUs and they are used about 30%, so 4 CPUs are roughly used in a second.
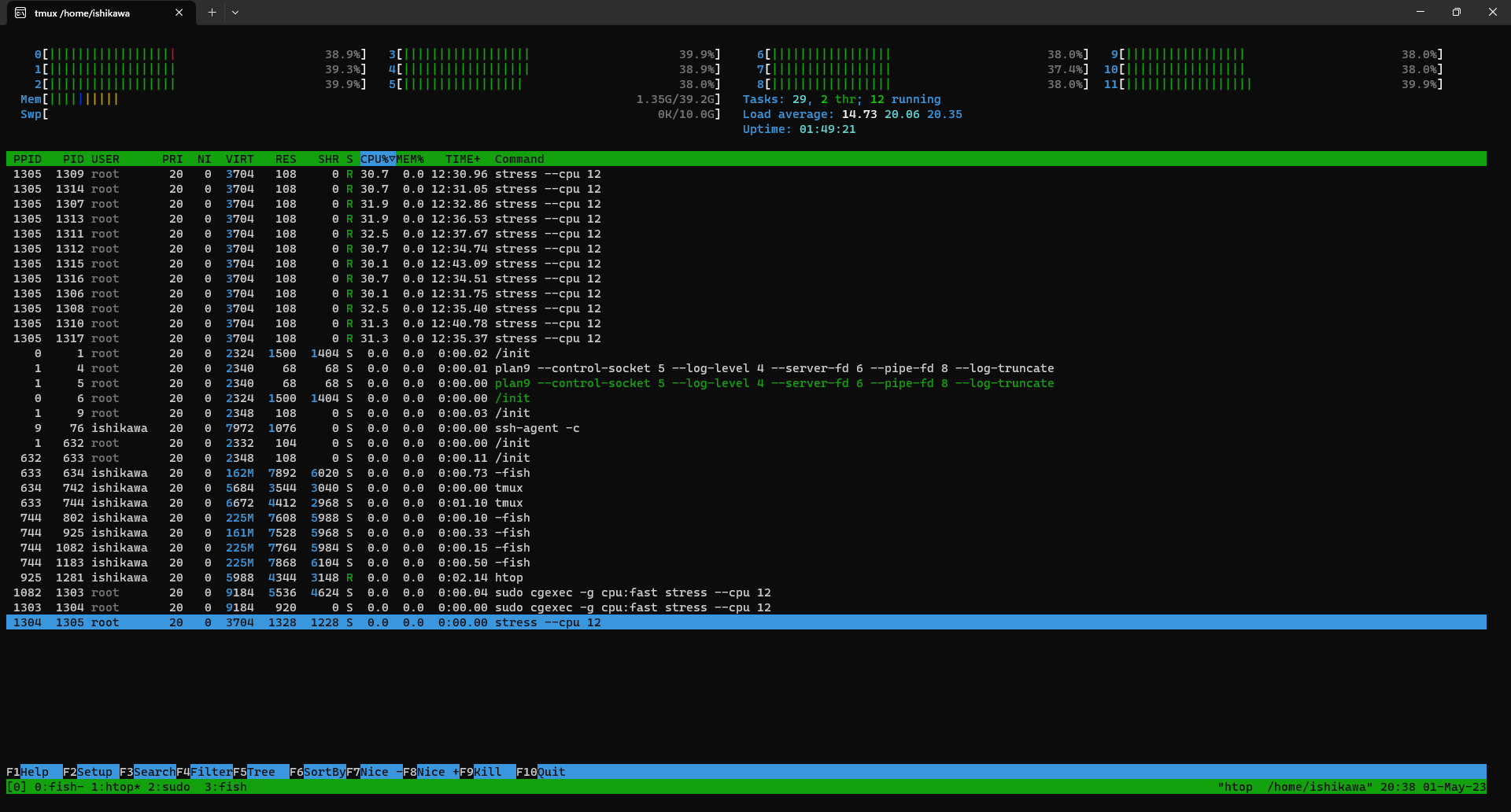
Cgroups for Memory
- Memory requests: It seems this is not used on Cgroup v1. I couldn’t find any document to use this.
- On Cgroup v2, it seems it sets
memory.minandmemory.low
- On Cgroup v2, it seems it sets
- Memory limit: sets
memory.limit_in_bytes
Questions
- How is it related to QoS?
- QoS is used to decide priorities to evict pods in the case of NodePressure